When Windows installs a new version, it leaves behind temporary files. These leftover files take space and can affect the installation of Windows Updates. Removing old Windows Update files frees up more disk space.
The operation is also an effective troubleshooting fix for Windows Update installation issues. This tutorial covers different methods to delete old Windows Update files on Windows 11 and Windows 10 computers.
- Windows Update Won’t Install Updates? How to Fix This Issue
- What To Do If Windows 10 Action Center Won’t Open
Contents
Is It Safe to Delete Windows Update Files?
Removing old Windows Updates files won’t cause any harm to your computer software or hardware components. Personal files aren’t deleted, either. It’s a safe process.
The only downside is that you may not be able to reverse or restore previous versions of Windows to your computer. A good rule of thumb is to delete Windows Update files only when:
- Storage space is low.
- Your PC fails to install Windows Updates.
How to Delete Old Windows Update Files
There are multiple ways to remove Windows Updates files on Windows computers. You can use built-in tools like Disk Cleanup and Command Prompt to get the job done. Likewise, you can also manually locate and delete temporary Windows Updates files.
We highlight four ways to get rid of Window Update files below. The steps may vary depending on your PC’s operating system version.
Delete Windows Update Files from Window Settings
Windows 11 and Windows 10 computers have a “Windows Update Cleanup” tool in the Settings menu. Follow the steps below to use the tool to delete old Windows Update files.
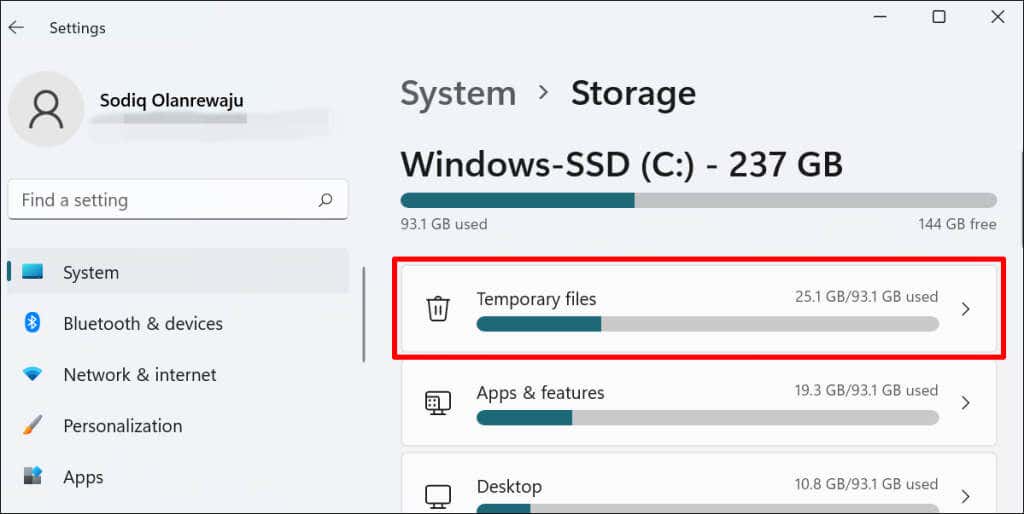
- In Windows 11, go to Settings > System > Storage and select Temporary files.
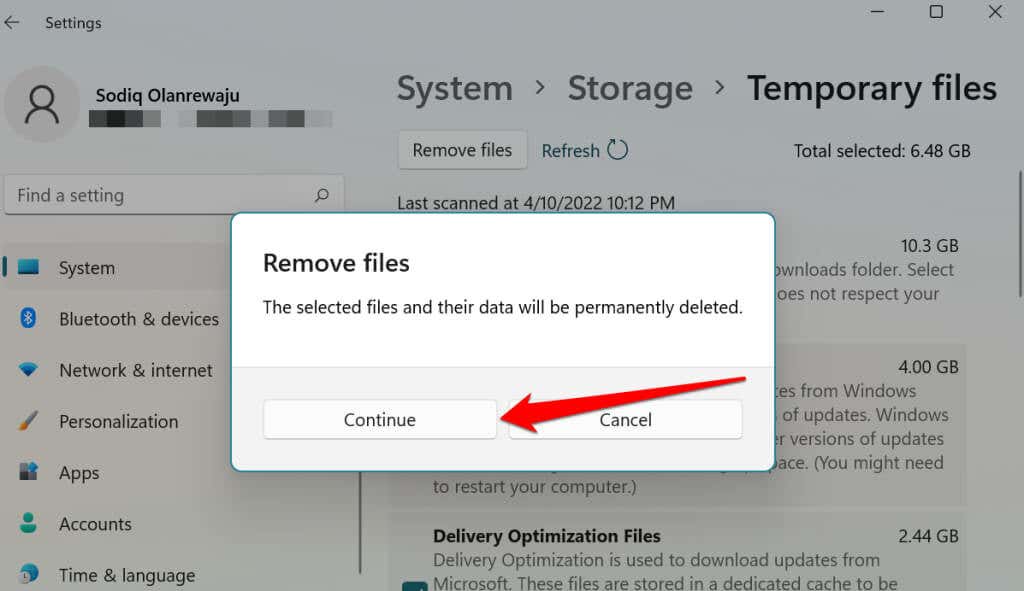
- Select the Windows Update Cleanup and Delivery Optimization Files checkboxes. Afterward, select the Remove files button at the top of the page.
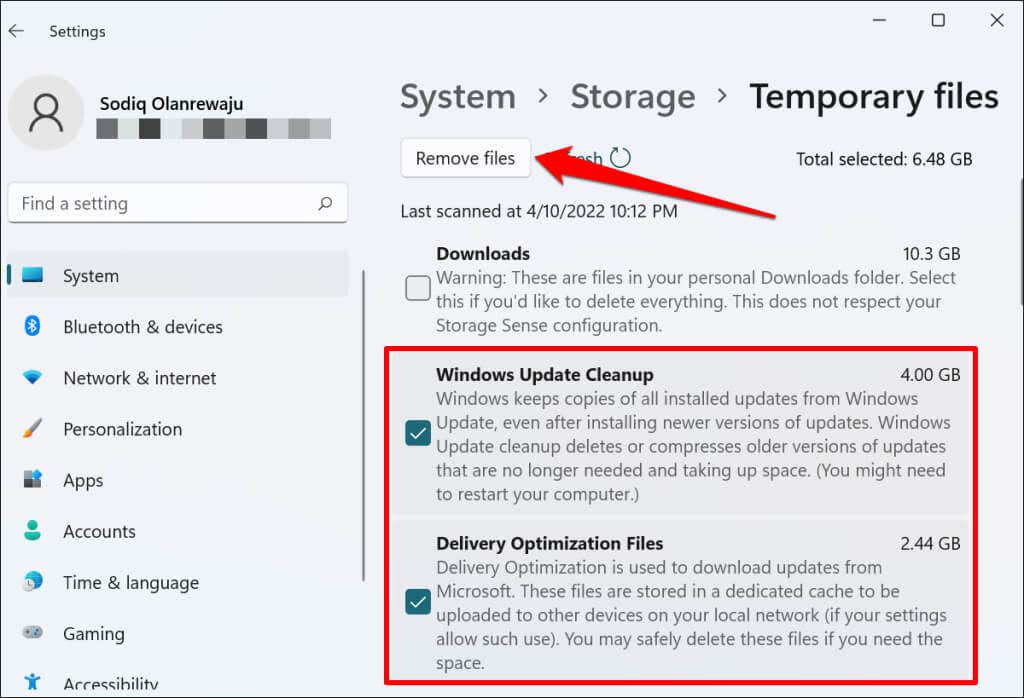
“Delivery Optimization Files” are associated with Windows Updates. The files allow your computer to exchange Windows Updates information with devices on your local network.
Although Windows automatically deletes Delivery Optimization files after a short period, manually removing them from your computer is safe. Microsoft recommends deleting the files to create free space on your hard drive.
- Select Continue on the confirmation to delete the Windows Update Files.
Note: For Windows 10, go to Settings > System > Storage > This PC > Temporary files > Previous version of Windows, and select Remove files.
Delete Windows Updates Files Using Disk Cleanup
Disk Cleanup is a built-in app for freeing disk space on Windows devices. It’s a compilation of unique tools for removing different file types eating up your PC’s storage space. You can use Disk Cleanup to delete temporary app files, empty your PC’s Recycle Bin, redundant internet files, etc.
Follow the steps below to use the Disk Cleanup app:
- Press the Start button, type disk cleanup in the search bar, and select Run as administrator below Disk Cleanup.
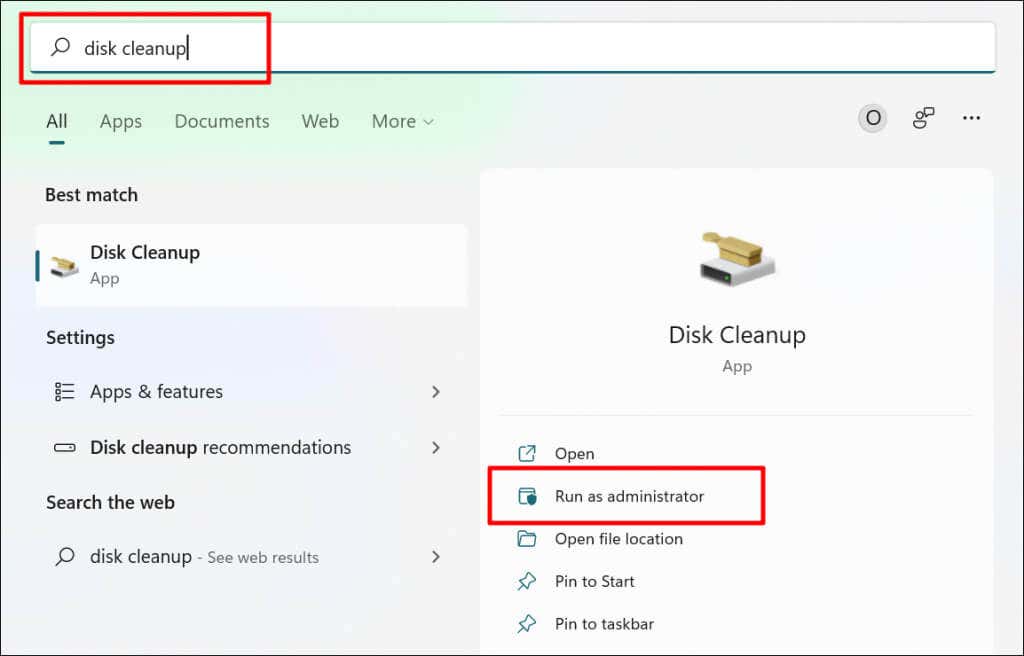
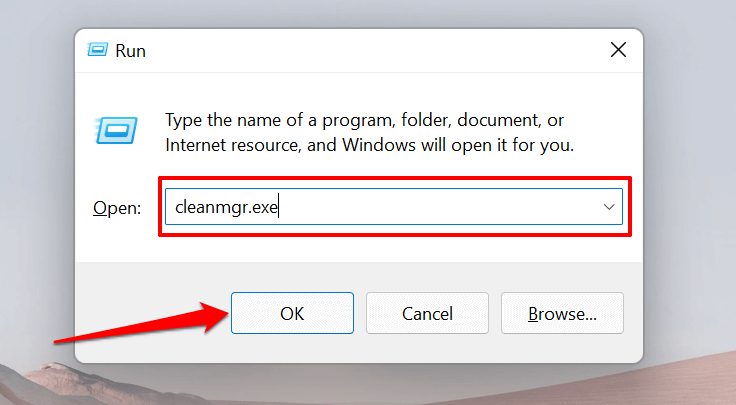
Alternatively, open the Windows Run box (press Windows key + R), type or paste cleanmgr.exe in the dialog box, and select OK.
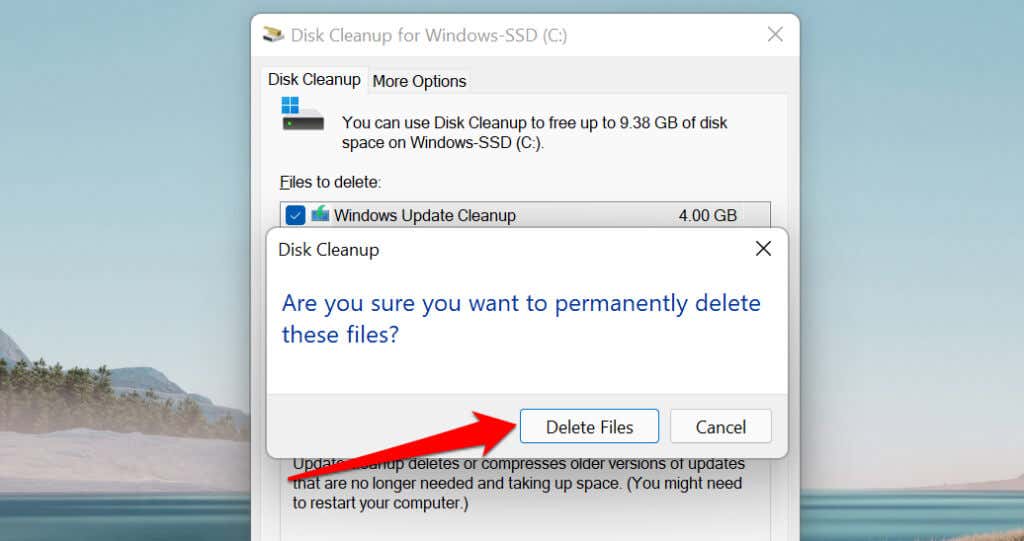
- Select the Windows Update Cleanup and Delivery Optimization Files checkboxes and select OK.
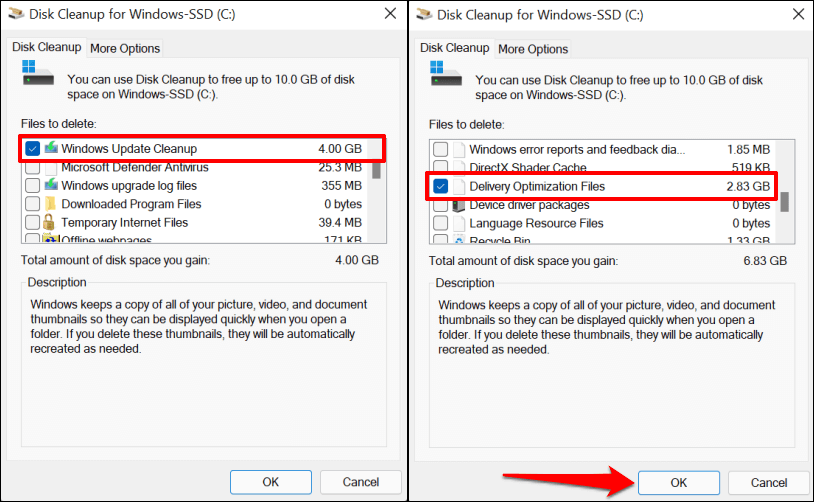
If you don’t see the “Windows Update Cleanup” option, you didn’t open Disk Cleanup with administrative privileges. Tap the Clean up system files button to unlock all Disk Cleanup features.
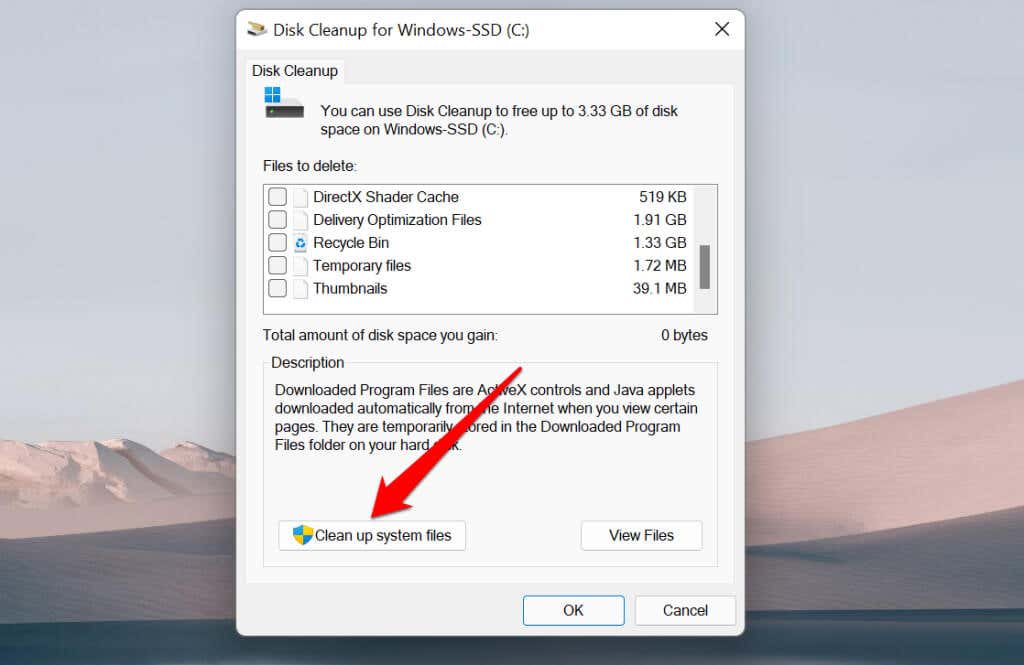
The Windows Update Cleanup option should appear in the Disk Cleanup app in a few seconds.
- Select Delete Files on the pop-up to proceed.
Manually Delete Windows Update Files
First, you need to stop the Windows Update service—the background service that detects, downloads, and installs updates for Windows and other programs.
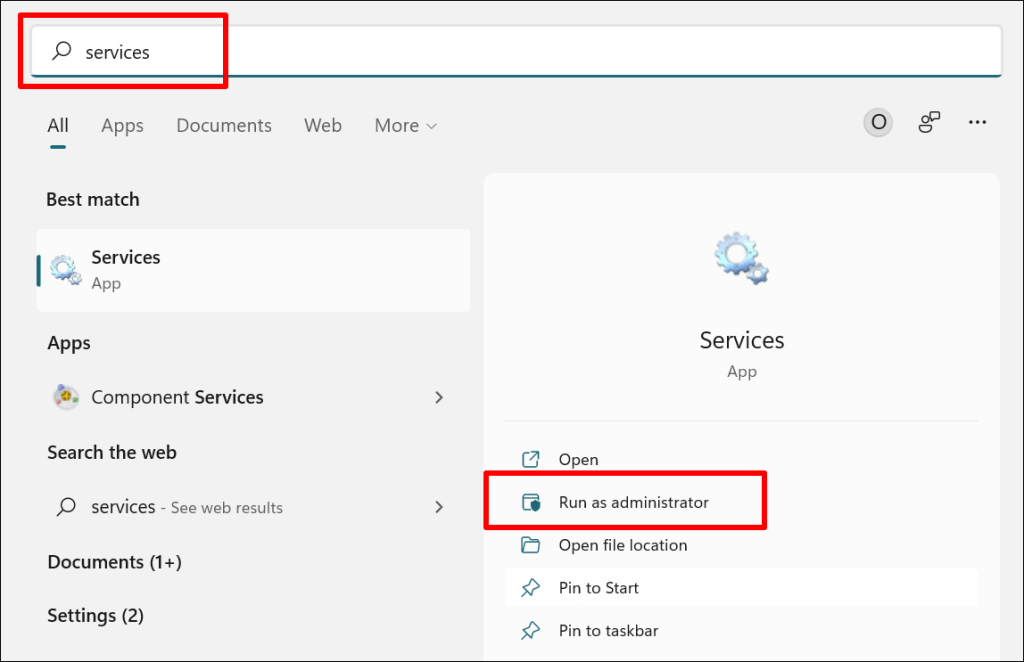
- Open the Windows Start Menu, type services in the search bar, and select Run as administrator below the Services app.
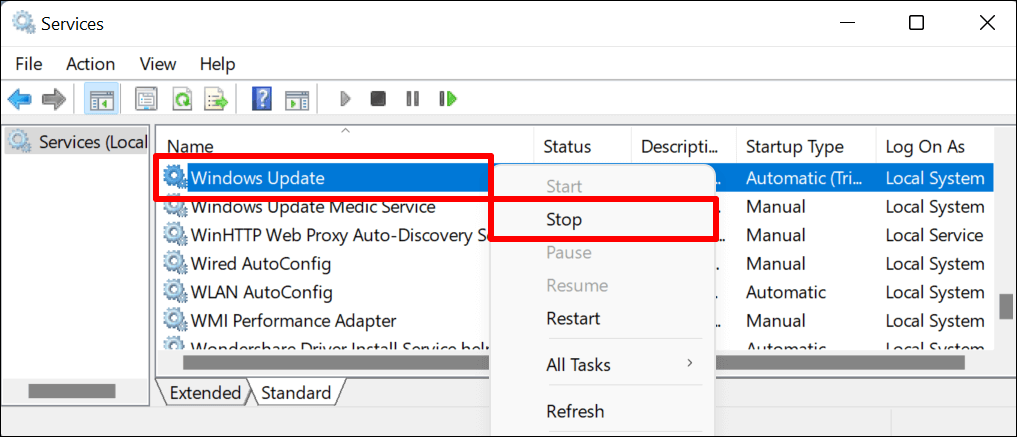
- Right-click on Windows Update on the list of services and select Stop.
- Open the File Explorer (press Windows key + E), paste C:WINDOWSSoftwareDistributionDownload in the Navigation Pane, and press Enter.
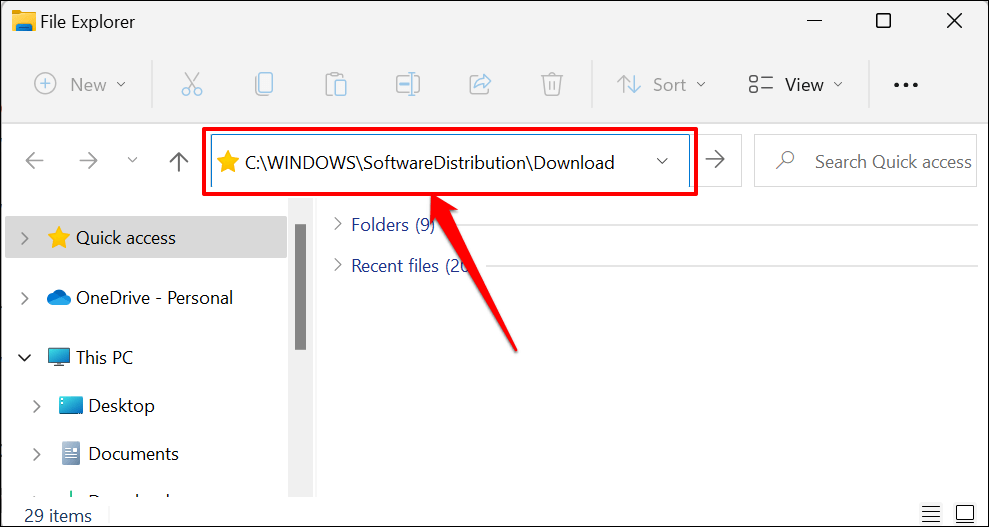
That’ll open the SoftwareDistribution folder—where Windows stores temporary installation files needed to update your computer’s operating system. Deleting or moving contents of the folder can also fix Windows Update issues.
- Press Ctrl + A to select all folders. Right-click the selection and select the Trash icon—or press the Delete key on your keyboard.
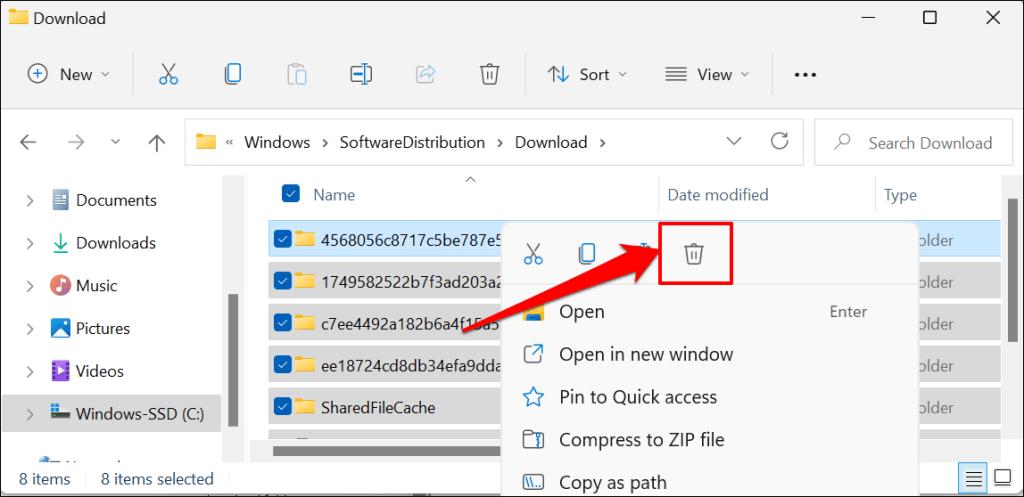
You can move the files to an external storage device if you don’t want to delete them. The final step is restarting the Windows Update service.
- Reopen the Windows Services app (see step #1), right-click Windows Update, and select Start.
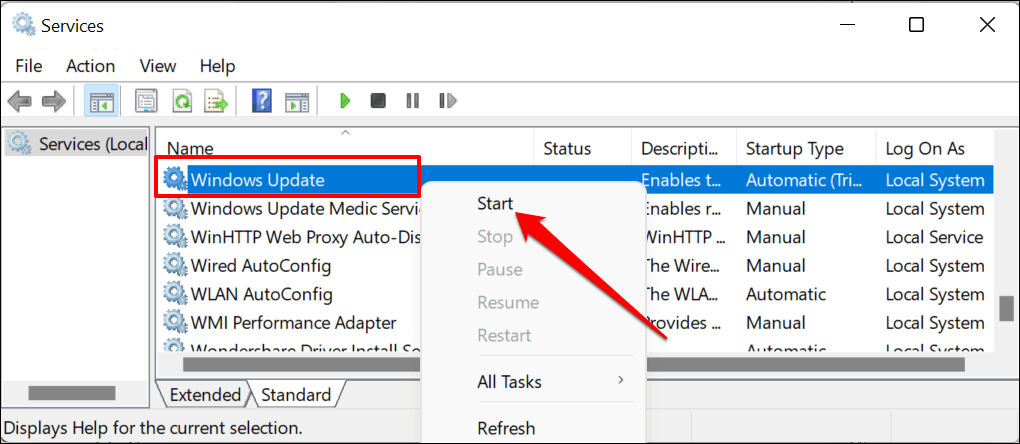
If a new Windows Update is available for your computer, Windows will download new files to the Software Distribution folder. The Windows Update temporary files are often large. If your PC is low on storage space, empty the folder after every Windows Update installation.
Delete Windows Updates Files Using Command Prompt
This method entails using Command Prompt to delete Windows Update cache files in your PC’s Software Distribution folder.
- Type command prompt or cmd in the Windows Search bar and select Run as administrator.
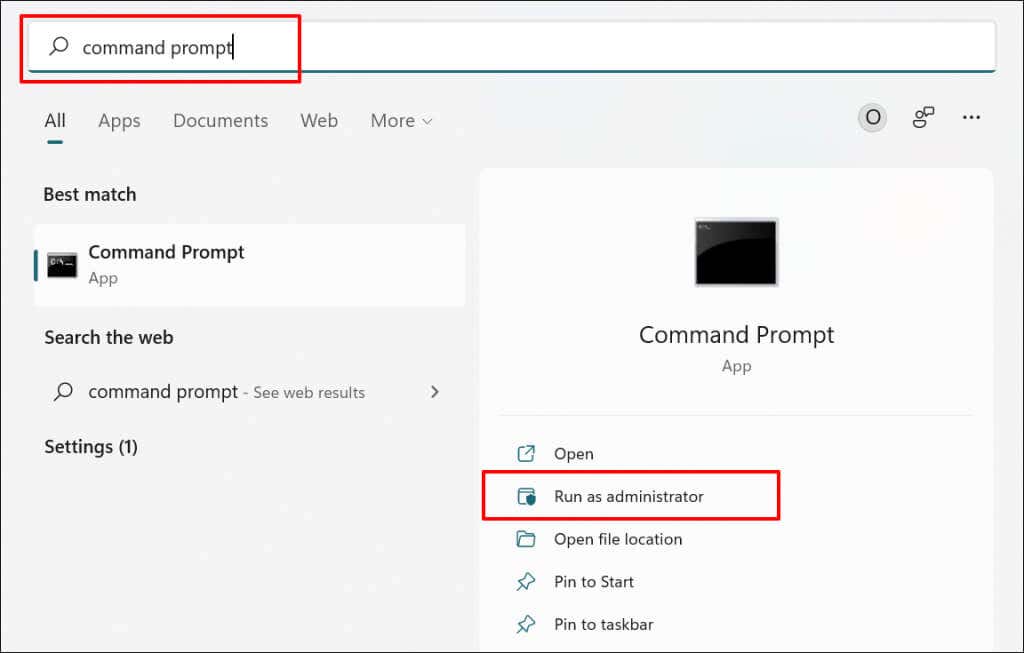
- Type or paste net stop wuauserv in the terminal and press Enter on the keyboard.
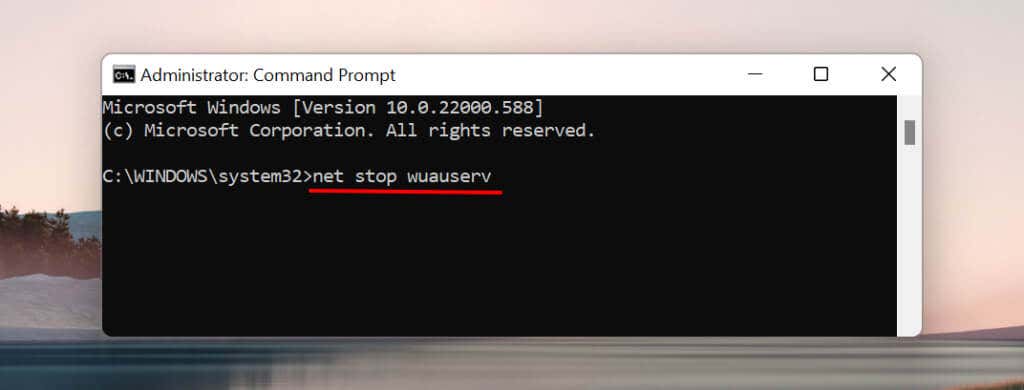
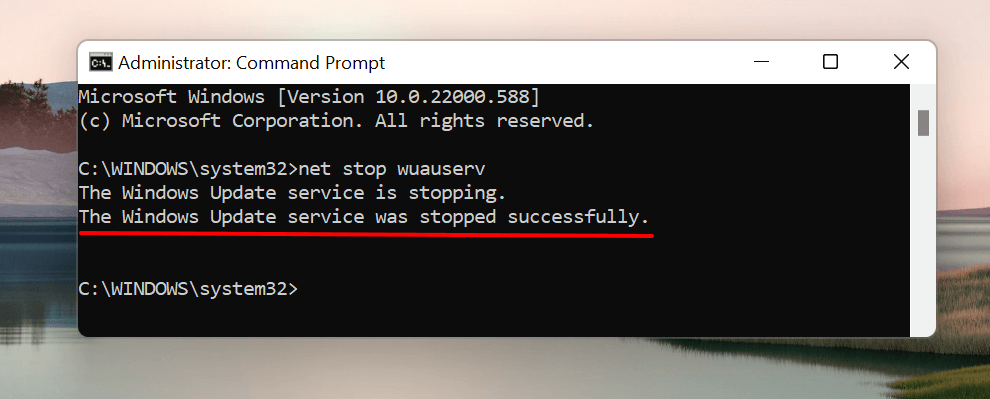
This command instructs Windows to stop the Windows Update service. Proceed to the next step when Command Prompt displays a “The WIndows Updater service was stopped successfully” message.
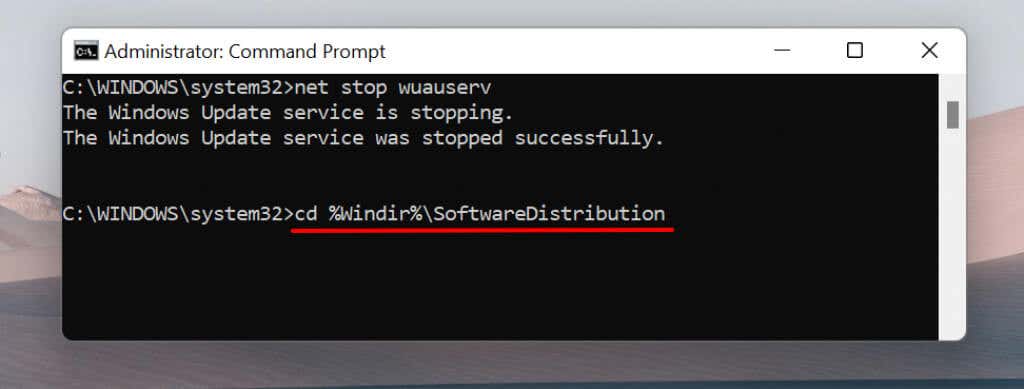
- Next, type or paste cd %Windir%SoftwareDistribution in the terminal and press Enter. This command opens the Software Distribution directory.
- Type of paste del /f /s /q Download and press Enter.
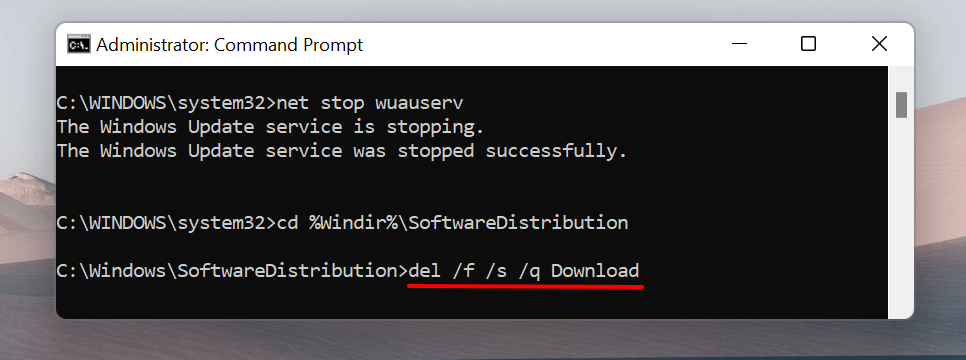
Command Prompt deletes the content of the Download folder in the assigned directory (i.e., SoftwareDistribution). The process might take a couple of minutes, depending on the size of the Windows Update files. Proceed to the next section when you get a success message.
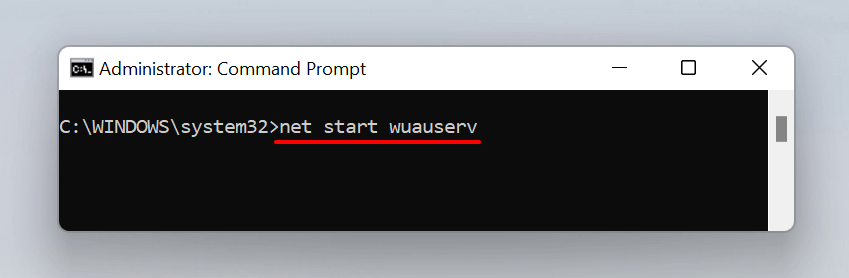
- Type or paste net start wuauserv in the console and press Enter to restart the Windows Update service.
Spoiled For Choice
My favorite thing about Windows is that there’s almost always more than one approach to executing an action. The four methods listed above will remove all downloaded Windows Update files on your PC. We recommend that you reboot your computer after deleting the files.





