The Windows Registry is a huge database containing configuration settings for programs, hardware, and applications running on your computer. Each time you install a program, its values and keys are embedded in the registry, from where you can configure or perform troubleshooting steps to repair a damaged program.
When the registry isn’t maintained properly, registry errors and corruption occur, causing lots of system and application problems in the operating system.


This guide will show you how the registry works, what causes registry errors, and offer some tried and tested solutions on how to fix registry errors in Windows 10 to get your computer working normally again.
Contents
How The Windows Registry Works
Whenever you install a new program on your computer, the registry receives a new set of instructions and file references, which are added in a specific location for the program.
The operating system constantly refers to it for more information such as file locations, the options to use with the program, when installing new software, altering your hardware, and so on.
Not all applications in Windows use the registry though. Some store their configurations in XML files while the portable type store data in executable files.
To access and configure the registry, you’ll use the Registry Editor, a free utility included by default with every Windows version since Windows 95.
This free registry editing utility isn’t the registry itself; it’s just a way through which you can view and make changes to it. You can access it via the Command Prompt, and execute the regedit command.
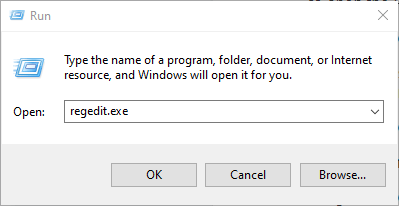
Alternatively, right click Start and select Run. Type regedit.exe and click OK or press Enter on your keyboard to open the Registry Editor.
Within the registry are registry values, registry keys, and registry hives. The registry values are instructions contained in registry keys, which are folders containing data. All these are found in several folders that categorize all registry data within subfolders, also known as registry hives.
When you make changes to the values or keys through the Editor, you actually change the configuration controlled by a specific value. This is why changes made to any setting are also made to the corresponding areas in the registry, though some of them don’t take effect until you restart your machine.
With this in mind, it’s important that you know what you’re doing each time you make any changes to the registry through the editor.
Note: Before you make any changes or fix broken registry items, make sure you backup the registry.
Common Causes of Registry Errors in Windows 10
There are several different ways that Windows Registry gets errors in it, and these aren’t the type that are solvable by a registry cleaner. In fact, registry cleaners don’t remove errors as such, just some unnecessary entries they find in the registry.
Some of the “errors” fixed by registry cleaners include empty or duplicate keys, unused values, and orphaned registry keys left over after you uninstall software from your computer.

The real registry errors, which indicate true problems with the registry of your computer’s operating system are the serious type that can cause issues such as a missing or corrupted registry, blue screen of death, preventing Windows from booting properly, or mention that Windows can’t access the registry.
In such situations, a registry cleaner is will fail to help fix registry errors in Windows 10. Plus, it can’t do anything at all without a working registry. Therefore, if you get such errors on your computer, don’t install a registry cleaner; it won’t fix registry issues.
As we’ve already stated, some causes of registry errors like registry fragments, duplicate keys, orphaned entries, and system shutdown errors are not worth worrying about.
However, if malware and viruses of any type attack and modify the registry, this is a huge problem and requires immediate attention and action. Viruses, spyware, and Trojans install registry entries that can’t be manually removed. They also prevent you from opening executable files by changing file associations, which is why you need to fix this type of registry error immediately.
Problems Caused By a Corrupt Registry
If your registry is corrupted, the computer may not restart. This usually happens when the computer is shut down, and you can’t track its cause because it unloads processes and drivers during shut down.
Power failure or unexpected shutdown can also corrupt the registry hives. In such cases, a process could’ve been modifying part of the registry hive and the unexpected shutdown or power failure abruptly stopped the process. Thus the registry hive is left in an inconsistent state, and when you restart your computer, the operating system will try loading the hive but find data that it can’t interpret, leading to error messages.
If your files are corrupted or you have faulty hardware that’s involved in writing to a disk like the processor, cache, RAM, or disk controller, these too can corrupt your registry and other system and data on your computer.
Registry corruption can also happen at shutdown, and you may not discover this until you try loading it at the next restart. In this case, the hive is written at shutdown, and the process may stop a component in the computer or the computer itself before the writing is fully completed.
How to Fix Registry Errors in Windows 10
- Back up your registry.
- Create a System Restore point.
- Restore your registry from the back up or restore point.
- Use the System File Checker to scan your registry.
Back Up Your Registry
Our ultimate guide on how to backup and restore the Windows Registry covers this in greater detail, but here’s a quick way to do it:
- To do this, right click Start and select Run.
- In the Run box, type regedit and click OK or press Enter on your keyboard.
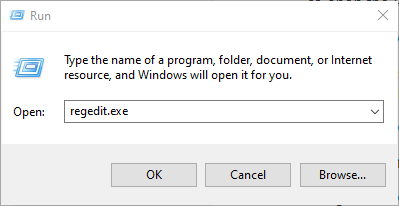
- In the Registry Editor window, right click Computer at the top left-hand side, and click Export.
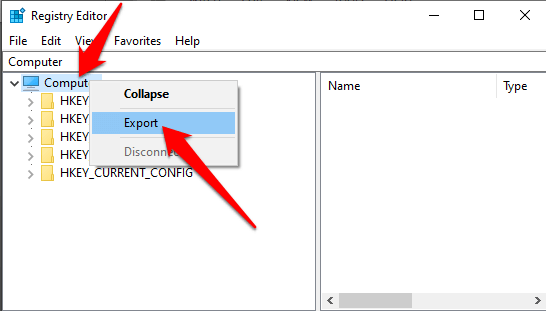
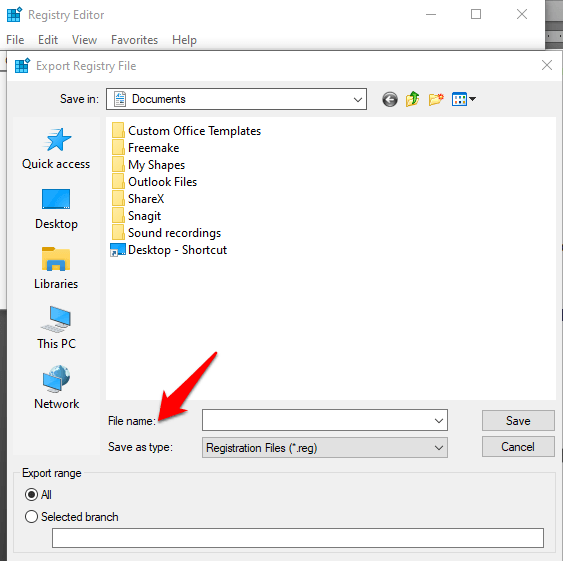
- Give the backup file a name and save it in a flash drive or cloud storage.
Create a System Restore Point
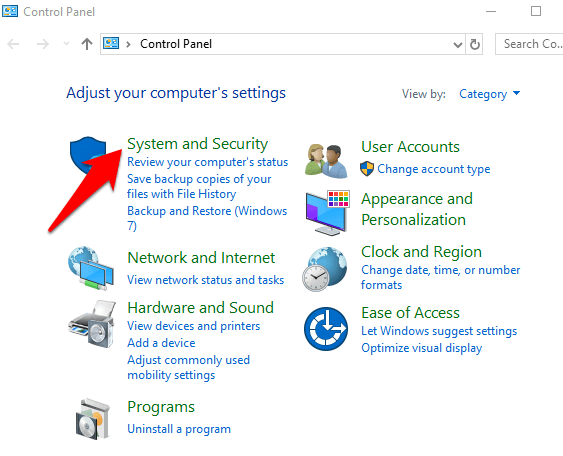
- To do this, open Control Panel and click System & Security.
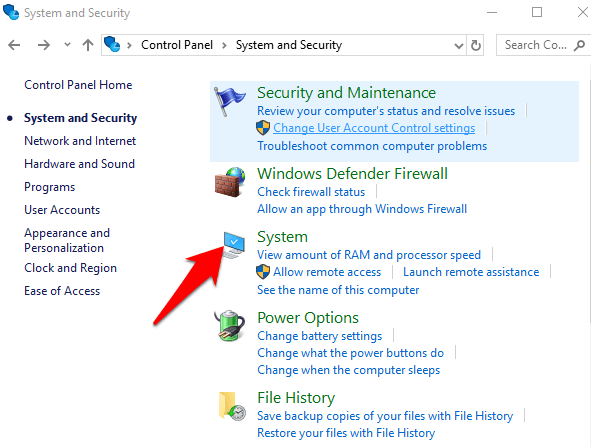
- Click System.
- On the left side, click Advanced System Settings.
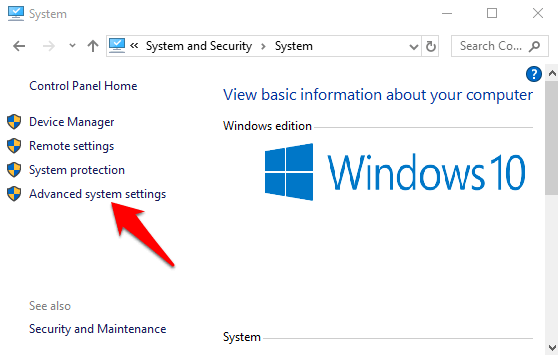
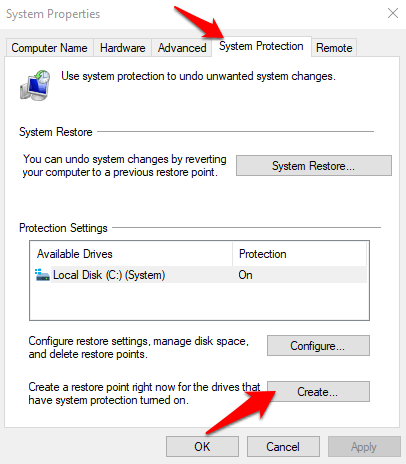
- Click System Protection tab, select Create, and press OK.
Restore Your Registry From The Backup Or Restore Point
- To do this, go back to the Run window (right-click Start>Run) and type regedit. Press OK or hit Enter.
- In the Registry Editor, click File>Import.
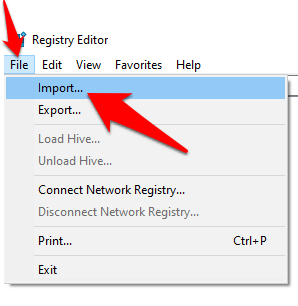
- In the Import Registry File popup, select where you saved the backup, click on the file and click Open.
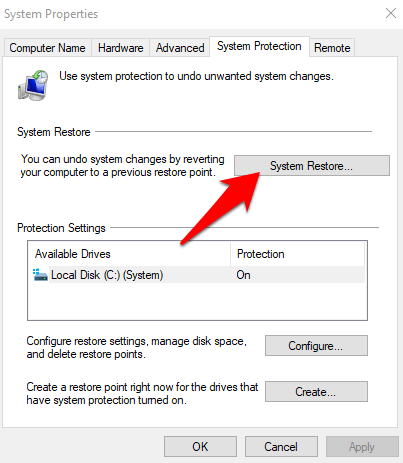
You can also restore it from the restore point.
- To do this, click Start and type create a restore point in the search bar.
- Select create a restore point from the results and then choose System Restore.
Use The System File Checker
The System File Checker (SFC) is a tool that checks your drive for any registry errors, and replaces faulty registries.
- To use this tool, open a Command Prompt and select Run as administrator.
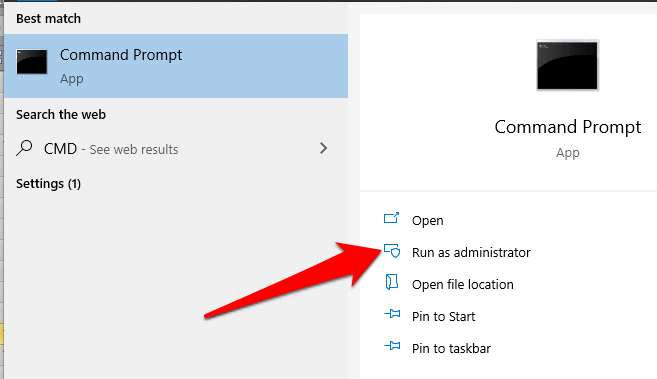
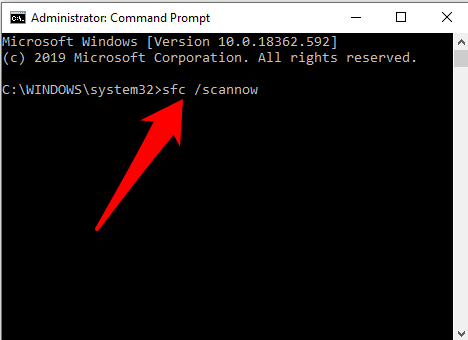
- Type sfc /scannow and press enter.
Preventive Measures
If you want a computer free of registry errors in future, here are some simple things you can do:
- Properly uninstall programs and apps you don’t use. A removal tool can help with this besides using the Add/Remove Programs window in Control Panel.
- Run regular virus scans and delete any malware or related files that install on your registry, causing programs in the system to crash.
- Remove unnecessary registry entries and repair missing file and ActiveX extensions using a registry cleaner.





