Do you share your work or home computer with others? Do apps and files from guest accounts consume an insane amount of disk space? Windows has a quota system that grants administrators more control over storage management. You can use the tool to set disk usage quota for both internal and external storage devices.
We’ll walk you through the steps to control data users can store on your PC by setting disk quota limits. Before jumping to the steps, note that the Windows Quota Management tool only works on drives formatted using the NTFS file system.

Contents
Configure Disk Quota via File Explorer
There are several ways to enable the quota management system in Windows 11. You can do so via File Explorer, Registry Editor, or the Group Policy Editor. However, the File Explorer route is the easiest.
- Open File Explorer and select This PC on the sidebar.
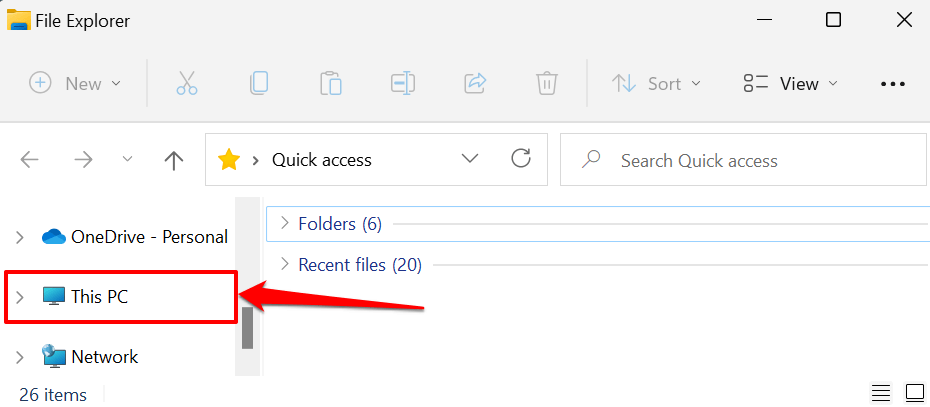
- Scroll to the “Devices and drives” section, right-click the disk you want to limit, and select Properties.
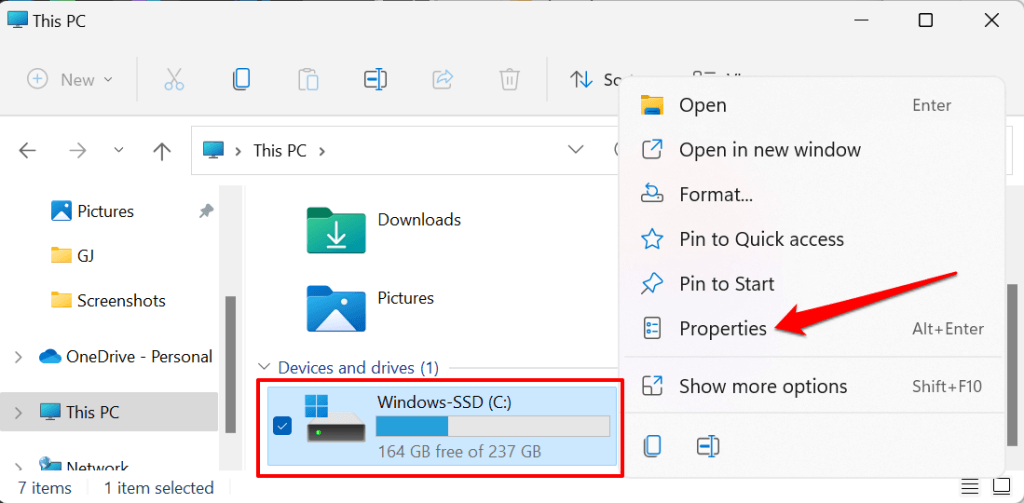
- Head to the Quota tab and select Show Quota Settings.
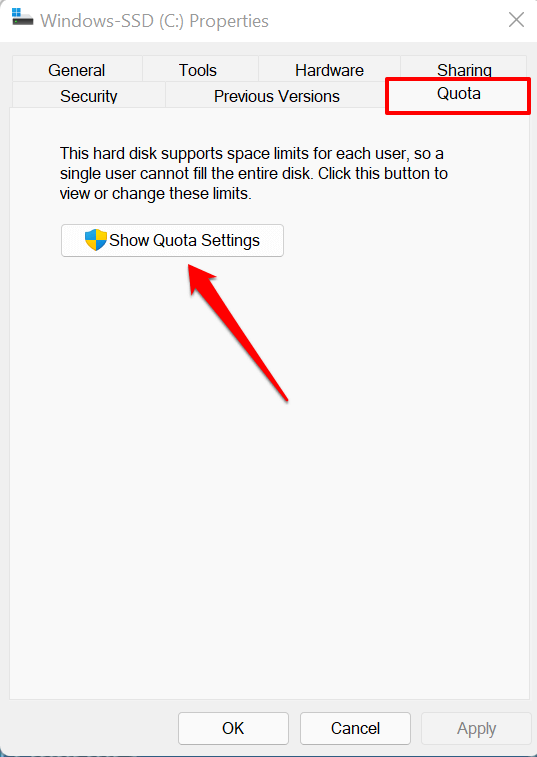
- Check the Enable quota management box.
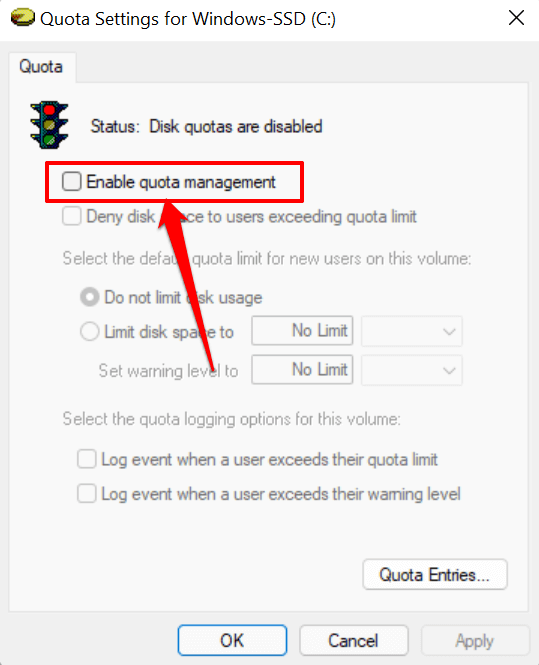
- Next, check the Deny disk space to users exceeding quota limit box. That will enforce the limitation and ensure any user who reaches the quota limit can no longer write data to the disk.
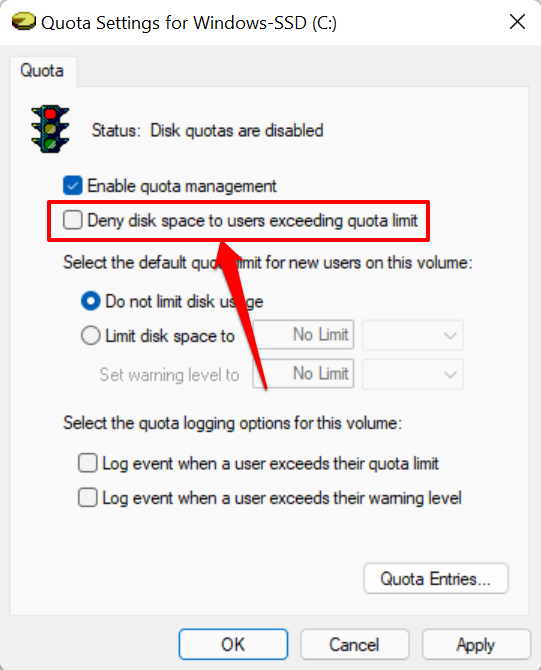
- Select Limit disk space to.
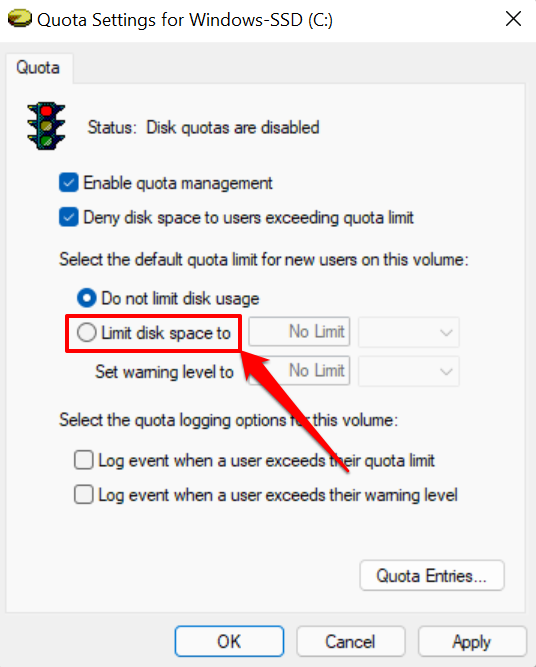
- The next step is to set the disk limit. Say you want to set a 30GB disk quota, enter the digit (30) in the first dialog box and select the storage unit (GB) in the adjacent drop-down box.
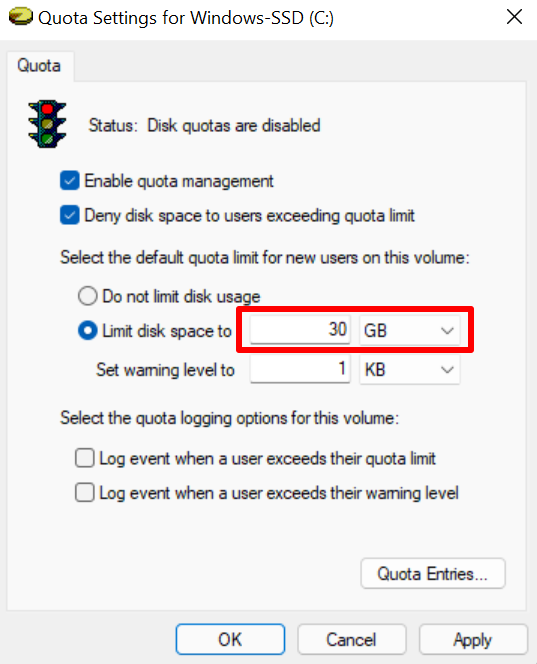
You should also set a warning level that’s slightly lower than the disk limit. For a 30GB disk limit, setting a 25GB warning level is ideal. When users hit or exceed the warning limit, Windows sends a reminder that they’re close to exhausting the disk space allocated to them.
- If you want Windows to record an event log (in the Windows Event Viewer) when users excess their disk quotas or hit storage limit, check Log event when a user exceeds their quota limit and Log event when a user exceeds their warning level.
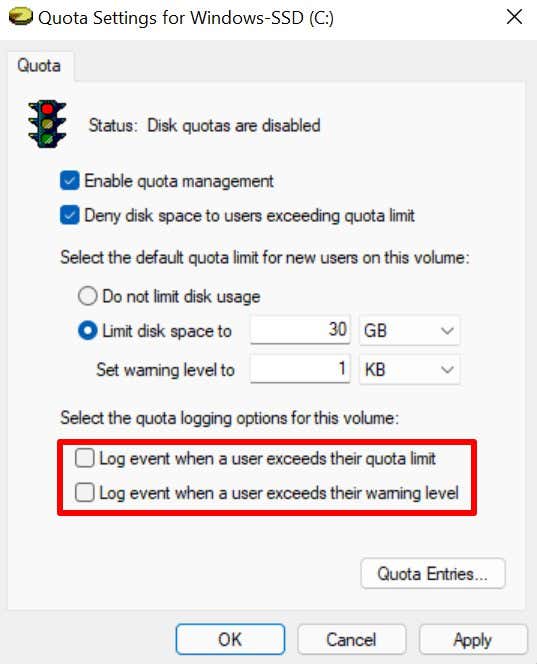
- Select Apply to proceed.
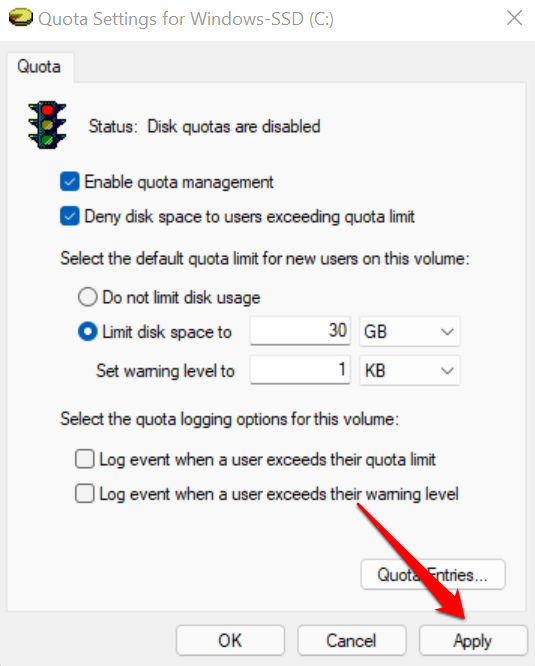
- Select OK on the warning prompt to enable the quota system you configured.
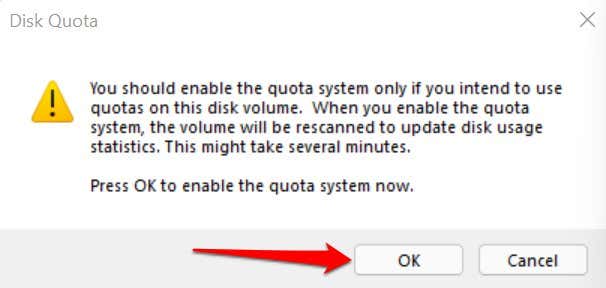
- Select OK in the Quota Settings window.
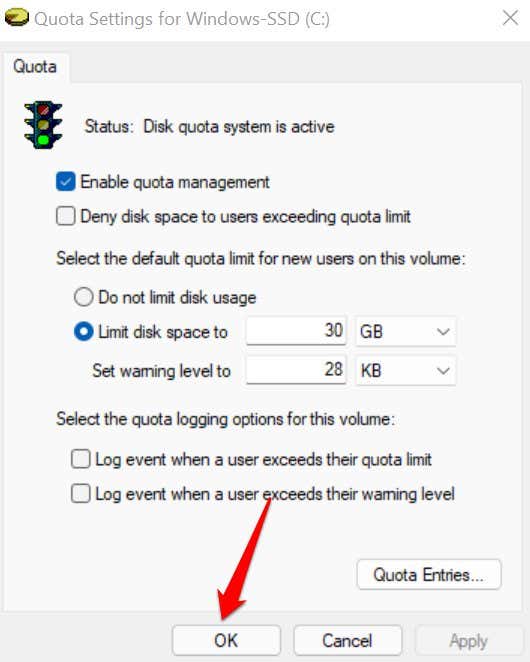
Note that you might have to restart your computer for these changes to take effect. We should also mention that disk quota configurations are drive-specific. If your PC has multiple disk partitions (separate from your C: drive), quota limits on the local disk don’t apply to other partitions.
View and Adjust Disk Quota Limit
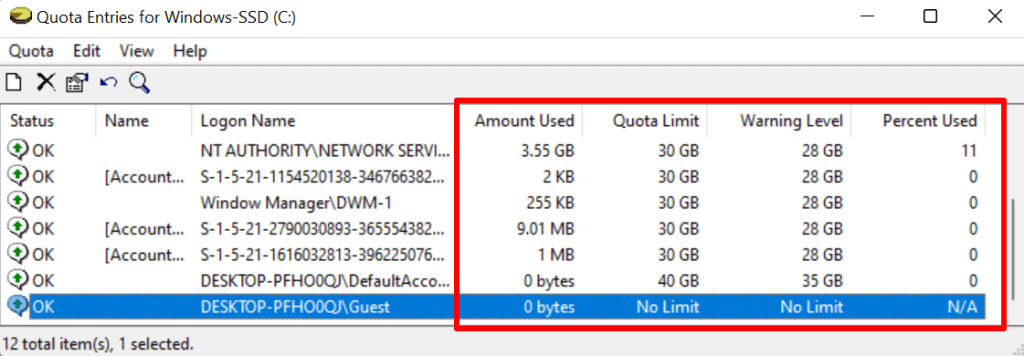
When you set a storage quota limit for disk, Windows applies the limit to all users on your computer. There’s a “Quota Entries” tool in the Quota Settings window that lets you adjust or disable the disk quota limit for specific users. You can also use the tool to check the current disk space usage for all user accounts against the set quota.
- Open the Quota Settings window for the drive and tap the Quota Entries button.
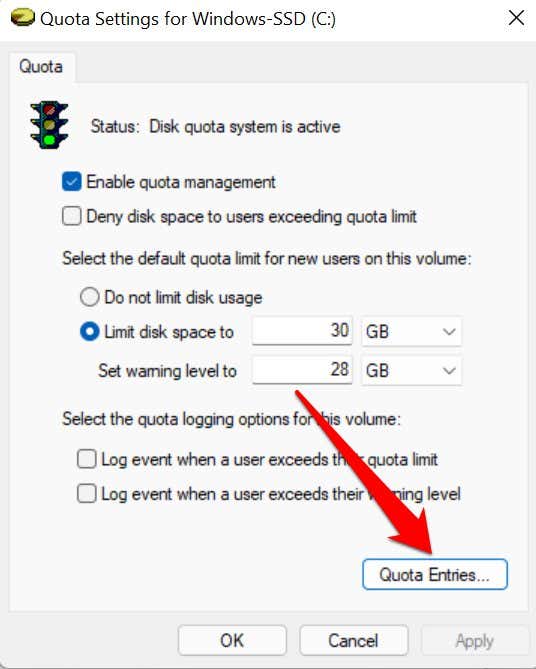
- The “Amount Used” and “Quota Limit” columns show how much disk space a user has consumed against their allotted quota limit.
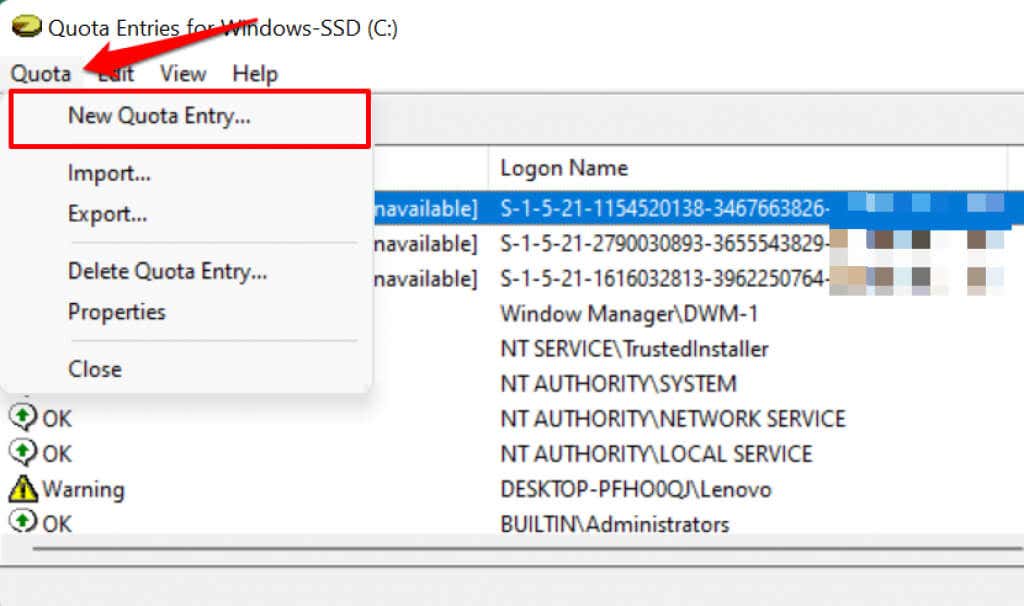
If you don’t find an account in the “Name” or “Logon Name” columns, proceed to add the user to the list manually. Tap Quota on the menu bar and select New Quota Entry.
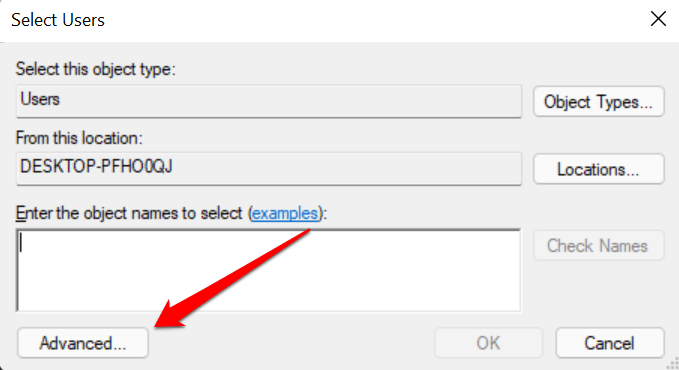
- Select Advanced in the bottom-left corner.
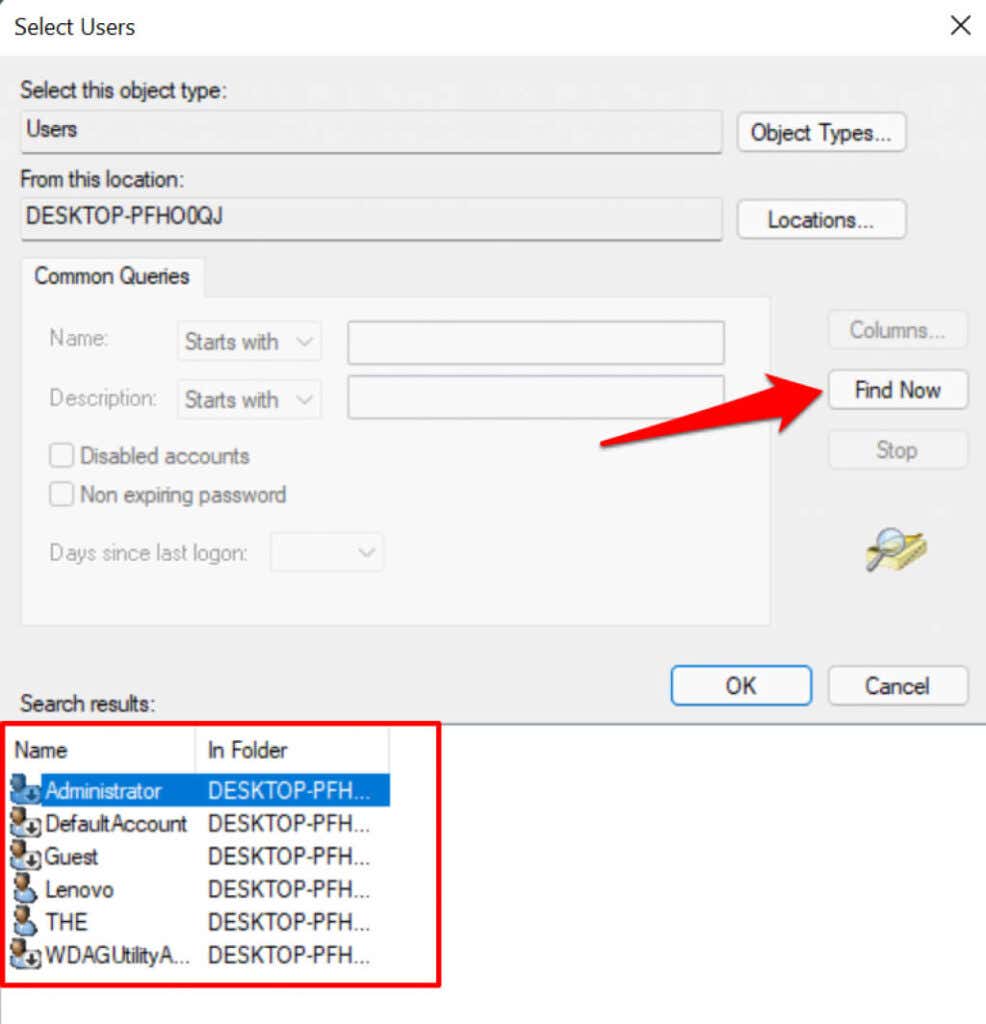
- Select the Find Now button and double-click the account you want to include in the storage quota limitation.
- Select OK to proceed.
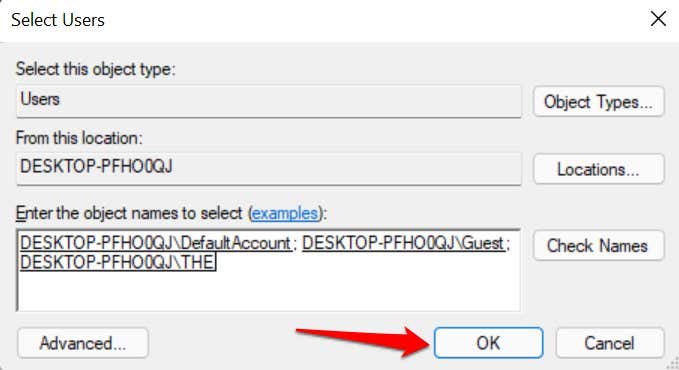
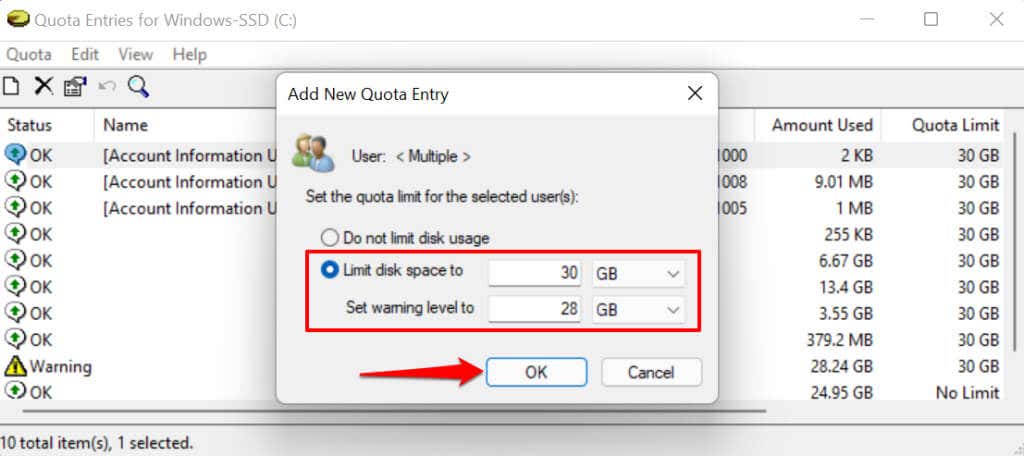
- Set the quota limit and warning level for the user and select OK.
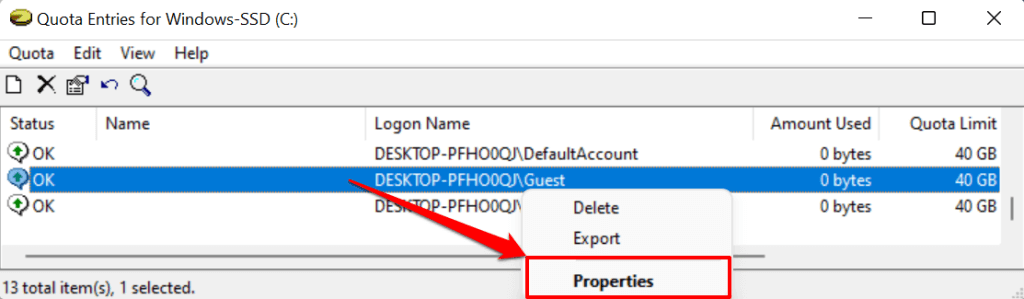
- To adjust or disable disk quota for a user, right-click the account and select Properties.
- Adjust the user’s disk quota in the Limit disk space to and Set warning level to dialog boxes. Select Apply and then OK.
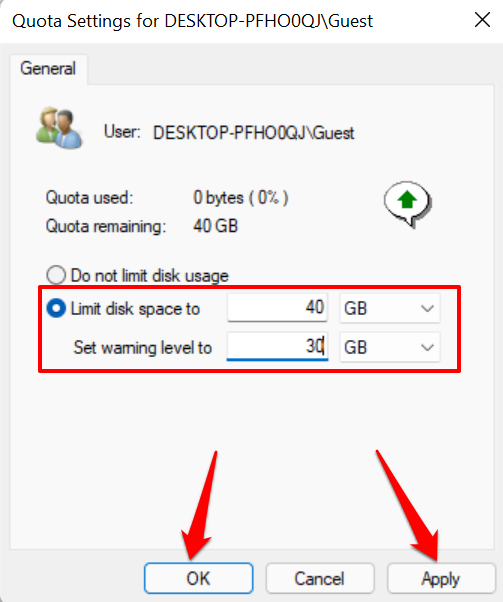
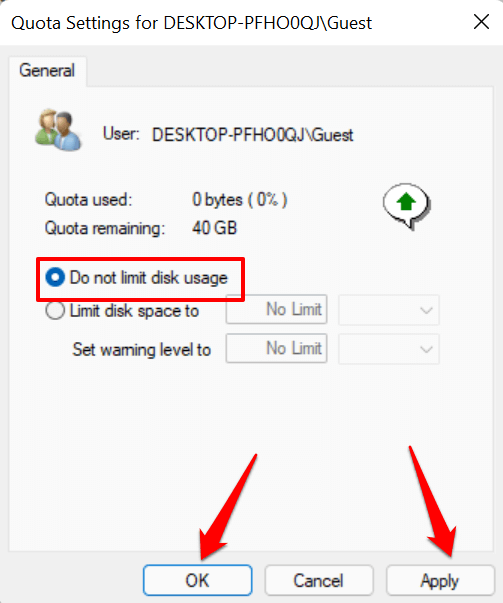
- Select the Do not limit disk usage radio button if you want to delete or remove the quota limit. Select Apply and OK to proceed.
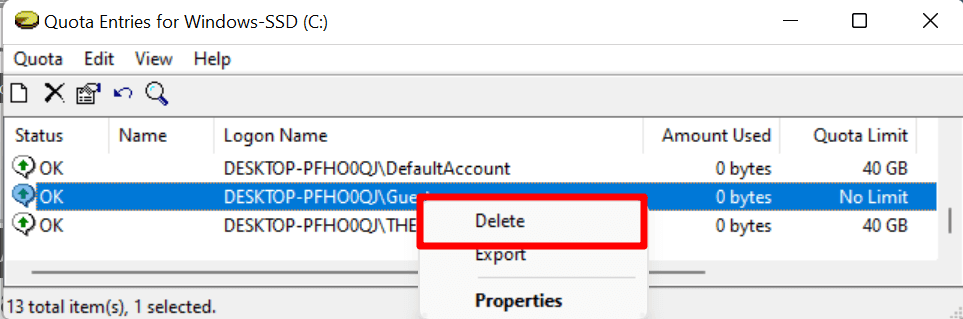
Another way to disable quota limits is to right-click the account name in the “Quota Entries” window and select Delete.
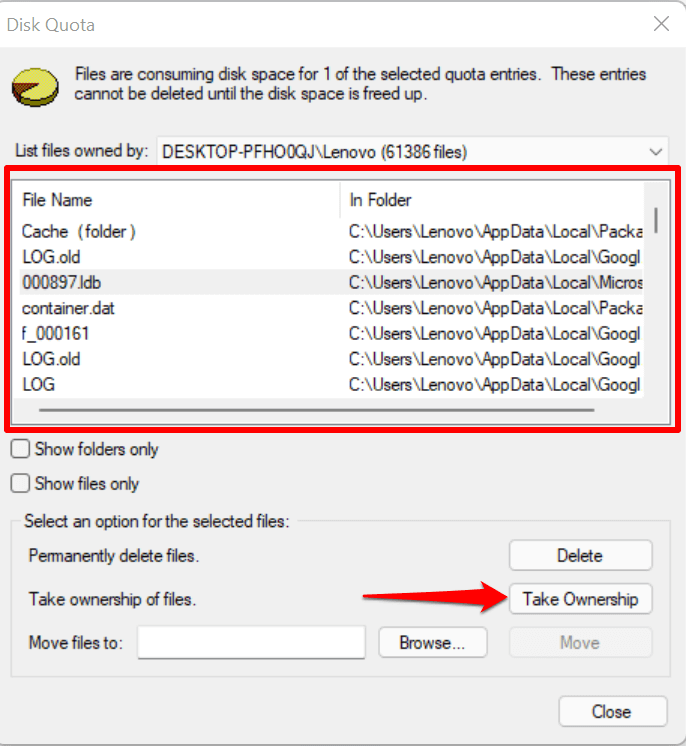
Select Take Ownership on the next page to save files in the disk space you allotted to the user account. Select Delete if you don’t need the files.
Set Disk Quotas Using Group Policy Editor
There are instances when Windows fails to enforce the storage quota limit configured via File Explorer. If that happens, modify or re-enable the disk quota in the Group Policy Editor.
Note that the Group Policy Editor is only available in Windows 11 Pro, Education, and Enterprise. If you use Windows 11 Home edition, try re-enabling the storage quota in the Registry Editor instead.
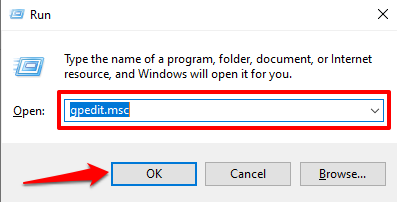
- Use the Window key + R keyboard shortcut to open the Windows Run box. Type gpedit in the dialog box and press Enter.
- On the sidebar, go to Computer Configuration > Administrative Templates > System and select the Disk Quotas folder.
- Double-click Enable disk quotas.
- Select the Enabled radio button, select Apply, and select OK to proceed.
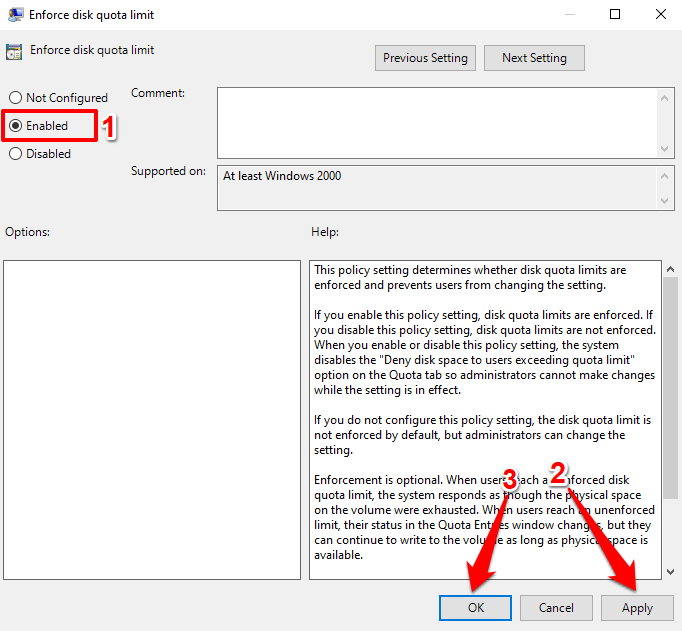
- One more thing: configure Windows to enforce the disk quota settings. Double-click Enforce disk quota limit.
- Select Enabled and select Apply to save the changes. Afterward, select OK to close the window.
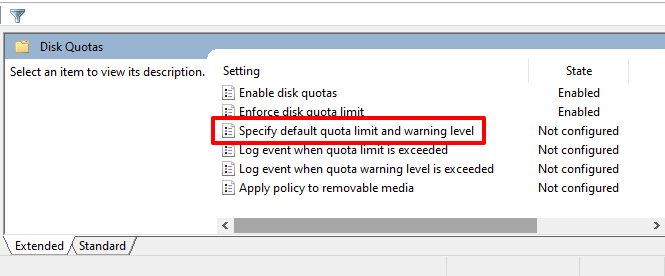
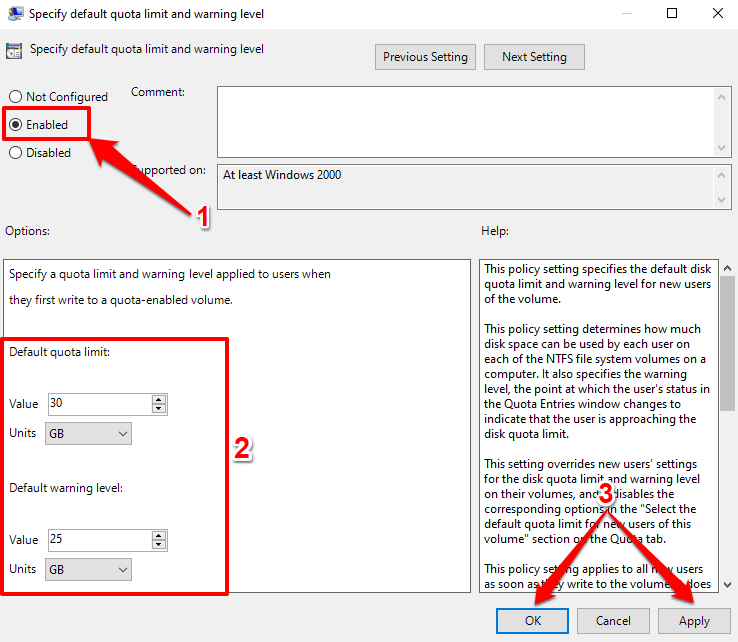
- The next and most crucial step is to specify your quota limit. Double-click Specify default quota limit and warning level.
- Select Enabled, enter the quota limit and warning level values and units, select Apply, and then OK.
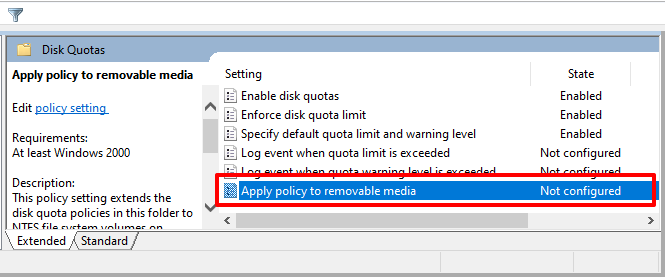
- If you want the disk quota configuration applied to removable or external drives, double-click Apply policy to removable media and set it to Enabled.
Set Disk Quota via Registry Editor
You can also force-enable a disk quota limit on Windows 11 devices via the Registry Editor. Ensure you make a backup of your PC’s registry files before proceeding, so you don’t damage any critical file that could corrupt Windows or break your PC.
- Press Windows key + R to open the Windows Run box. Enter regedit in the dialog box and select OK.
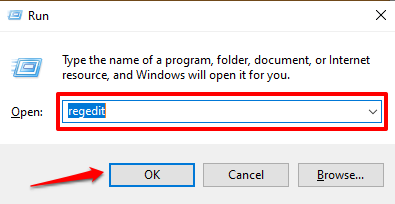
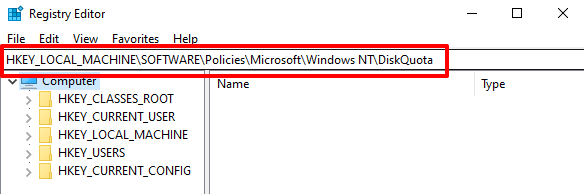
- Paste HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINESOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoftWindows NTDiskQuota in the address bar and press Enter.
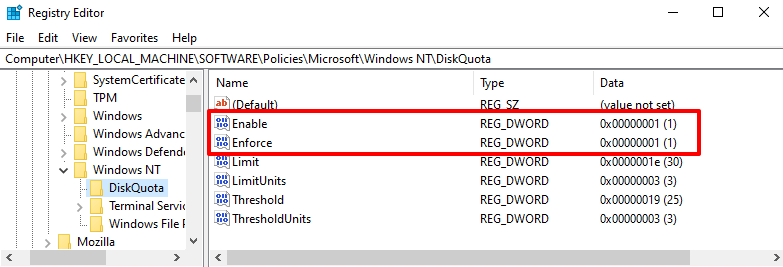
Ensure the Enable and Enforce registry keys and their values are set to 1 (i.e., enabled). They both enable and enforce the disk quota limit in Windows.
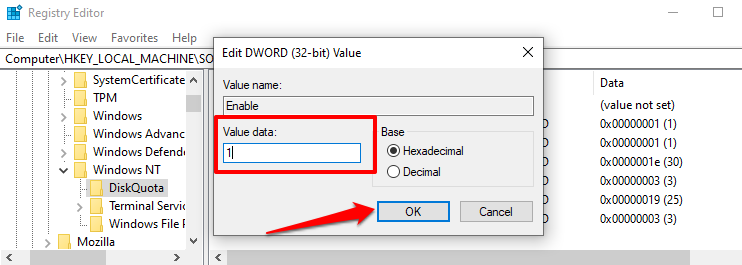
- Double-click the “Enable” or “Enforce” registry keys, enter 1 in the “Value data” dialog box and select OK.
Automate Storage Management
With the steps in this tutorial, you can set up a disk quota management system in Windows 11. These methods are backward compatible with older versions of the Windows operating system. That is, you can adopt these steps to set disk quotas in Windows 10, Windows 8, and Windows 7.





