There are plenty of Windows system processes with long, confusing names, from the WMI Provider Host to the Client Server Runtime. If you ask most Windows users what they do, however, they won’t know. That’s because these system processes are designed to work, but not be seen (unless there’s a problem).
The Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation process is further proof of this, with a long name, but not much indication (beyond audio) what it might be doing on your Windows PC. To help you understand what it does, here’s everything you need to know about the Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation process in Windows 10.

Contents
- 1 What Is Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation in Windows 10?
- 2 Is Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation Safe?
- 3 How to Troubleshoot Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation High CPU Usage Issues
- 4 How to Check Whether Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation Is a Genuine System Process
- 5 Understanding Windows System Features
What Is Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation in Windows 10?
The Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation process (or audiodg.exe) is an important component in the Windows operating system. As the name might suggest, it plays an important part in how audio output is handled by Windows PCs.
The audiodg.exe process is the audio engine for Windows, allowing third-party services access to your sound output devices. It also has responsibility for audio enhancement features, like Windows Sonic for Headphones, which helps to improve audio quality for headphones.
It provides access to Windows audio that other apps, services, and developers can use. Audio products, like headphones, could come with their own enhancement software—these apps will use the Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation process, rather than interfacing with the Windows Audio service directly.
In some cases, you may find that the Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation service is replaced with another digital signal processor from a hardware manufacturer (such as Creative). This isn’t anything to be alarmed about, but if you don’t recognize the hardware, you can check and remove any potential malware quickly.
The audiodg.exe process offers greater security and stability, as an unstable app or service crashing the separate Windows Audio service could cause a Blue Screen of Death (BSOD) error. With audiodg.exe taking control of Windows’ digital signal processing features, this is much less likely to occur.
It also gives you the ability to disable enhancements without affecting Windows Audio settings elsewhere.
Is Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation Safe?
It isn’t usually a good idea to disable important system processes like the Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation process. Disabling it will require you to disable the main Windows Audio service, which will cripple all Windows audio output. However, this would leave you without sound.
Thankfully, audiodg.exe is entirely safe to leave running. In most cases, it shouldn’t cause any issues, with minimum system resources used.
Most issues with the Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation service can usually be traced to third-party apps or services that may be accessing it. If you’ve installed new hardware recently, along with audio control software, then the additional enhancements being used could result in instability and high CPU usage.
If that’s the case, then you can disable all Windows audio enhancements. This should cause the CPU usage to return to normal and leave the audiodg.exe process without much to do, remaining active, but otherwise silent.
There can sometimes be problems with malware pretending to be other services, like the audiodg.exe service, although this is unlikely. If you’re worried, you can quickly check if this is the case by following the steps in a section below.
How to Troubleshoot Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation High CPU Usage Issues
Most of the time, the audiodg.exe process should run without issue. You should only see it using system resources when audio enhancements are activated by a third-party app or service, and should quickly return to zero usage.
However, if you spot Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation with high CPU usage that doesn’t return to normal, this could point to a problem with your audio settings and enhancements. First, check that no third-party audio software is running on your PC, including audio control software from hardware manufacturers.
That also includes any audio enhancement software like equalizers, surround sound management, and audio mixers that you may have installed. Software like this can cause CPU usage spikes in the audiodg.exe process.
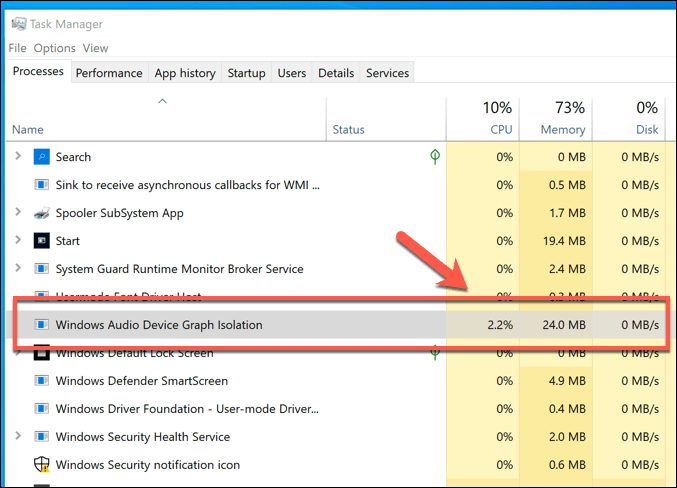
If you find software like this running, close it and ensure that it’s no longer running in Windows Task Manager. If your system resources don’t return to normal after this point, then Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation high CPU usage can usually be resolved by disabling audio enhancements entirely.
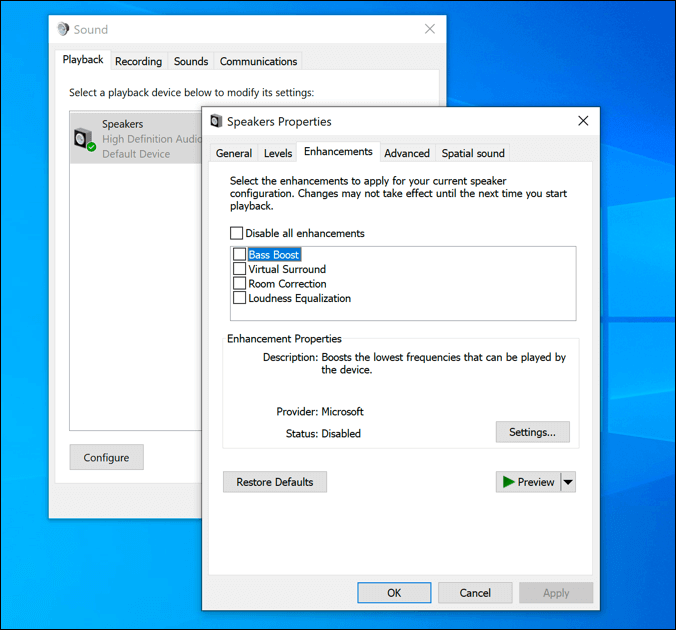
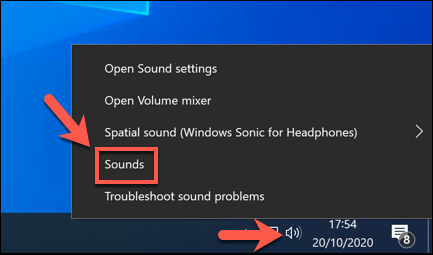
- To do this, find the speaker system tray icon in the notifications area on your taskbar. Right-click it, then select the Sounds option.
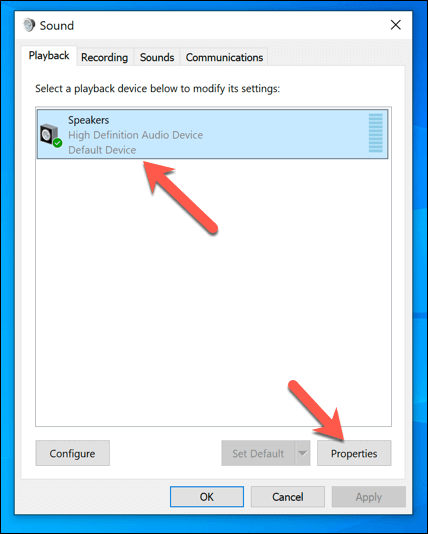
- In the Playback tab, select your audio output device, then select the Properties button.
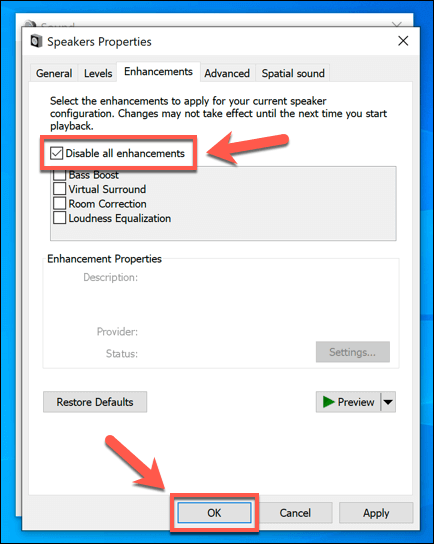
- In the Enhancements tab of the Properties window, you’ll see a list of available enhancements. Select the Disable all enhancements checkbox to switch these off, then select OK to apply the new settings.
This should disable the audio enhancements and return the audiodg.exe process to normal. If it doesn’t, you may need to run the Windows Troubleshooter to investigate audio issues instead.
- To run this, right-click the Start menu and select the Settings option.
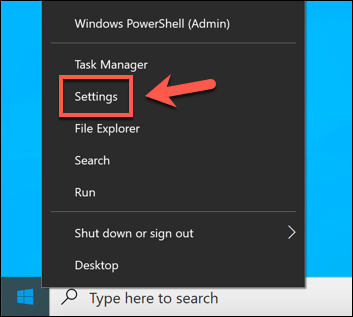
- In the Settings menu, select Update & Security > Troubleshoot > Additional troubleshooters > Playing audio > Run the troubleshooter. This will launch the Windows Troubleshooter tool for Windows Audio and all related services and processes.
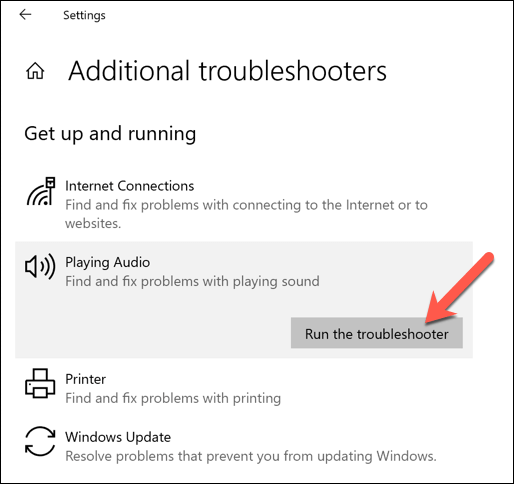
Windows Troubleshooter will automatically scan for and attempt to fix any problems with your Windows Audio settings and services, including audiodg.exe. It will also list any problems that it detects but can’t fix itself, allowing you to troubleshoot manually.
How to Check Whether Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation Is a Genuine System Process
Reports of malware hiding as system processes are uncommon, but it has been known to happen. If you want to be sure that the Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation process is a genuine system process, you can do so using Windows Task Manager.
- Right-click the taskbar and select the Task Manager option to begin.
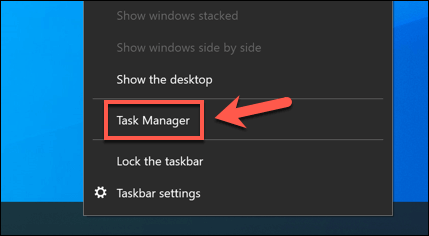
- In the Task Manager window, right-click Windows Audio Device Graph Isolation in the Processes tab (or audiodg.exe in the Details tab), then select the Open file location option.
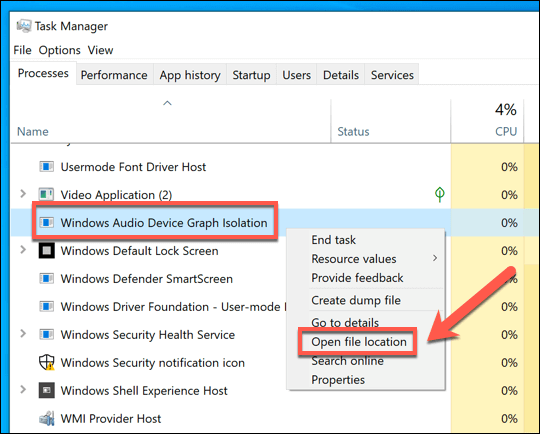
- This will open Windows File Explorer. If the location of the audiodg.exe file is in the C:WindowsSystem32 folder, you can be confident that this is a genuine Windows process.
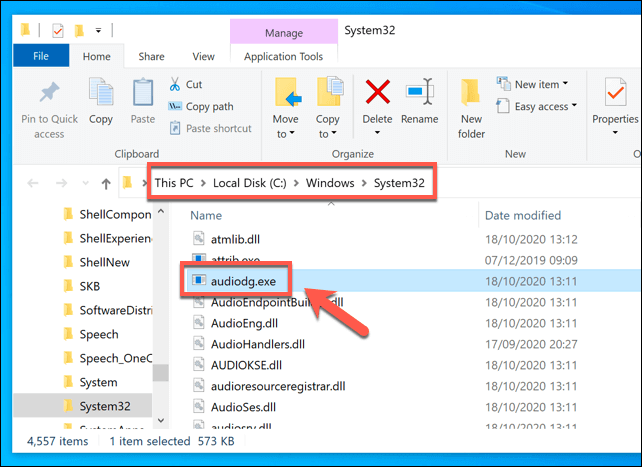
If the file is elsewhere, however, then this could indicate a likely malware infection, which you’ll then need to scan and remove it using Windows Defender or a third-party alternative.
Understanding Windows System Features
Processes like audiodg.exe and msmpeng.exe should, in most cases, work fine without any additional input. As Windows system processes, they act to provide the many features that you’ll see on your PC, and shouldn’t be a cause for concern. If you’re still worried, a quick malware scan should help put your mind at ease.
When system processes do show issues, it can usually be resolved through regular system maintenance. High CPU spikes can be monitored for problems, with solutions like fixing your computer fans helping to reduce the demands on your PC. If all else fails, considering upgrading your PC to give Windows extra resources.